"""
Understanding GIS: Practical 5
@author jonnyhuck
Calculate the distortion on a projected map
References:
Canters et al. (2005): http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.557.5040&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Gosling & Symeonakis (2020): https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/15230406.2020.1717379
https://pyproj4.github.io/pyproj/stable/examples.html
https://pyproj4.github.io/pyproj/stable/api/crs/crs.html
https://pyproj4.github.io/pyproj/stable/api/transformer.html
https://pyproj4.github.io/pyproj/stable/api/geod.html
New Topics:
Translating Equations & Text into code
Random numbers
Numpy
"""
from numpy import arange
from numpy.random import uniform
from matplotlib.patches import Patch
from math import hypot, sin, cos, radians
from pyproj import Geod, CRS, Transformer
from geopandas import read_file, GeoSeries
from shapely.geometry import Point, Polygon
from matplotlib.pyplot import subplots, savefig
from matplotlib_scalebar.scalebar import ScaleBar
def offset(x, y, distance, direction):
"""
* Offset a location by a given distance and direction
"""
x2 = x + cos(radians(direction)) * distance
y2 = y + sin(radians(direction)) * distance
return (x2, y2)
def evaluate_distortion(g, transformer, minx, miny, maxx, maxy, sample_number):
"""
* Calculate a selection of distortion measures, based on Canters et al. (2005)
* and Gosling & Symeonakis (2020)
"""
''' FINITE AREAL AND SHAPE DISTORTION - Canters et al. (2005) '''
# calculate the required number of random locations (x and y separately) plus radius
xs = uniform(low=minx, high=maxx, size=sample_number)
ys = uniform(low=miny, high=maxy, size=sample_number)
rs = uniform(low=1000, high=1000000, size=sample_number)
# offset distances
forward_azimuths = arange(0, 360, 22.5)
n = len(forward_azimuths)
# loop through the points
planar_areas = []
shape_indices = []
ellipsoidal_areas = []
for x, y, r in zip(xs, ys, rs):
# construct a circle around the centre point on the ellipsoid
lons, lats = g.fwd([x]*n, [y]*n, forward_azimuths, [r]*n)[:2]
# project the result, calculate area, append to the list
e_coords = [ transformer.transform(lon, lat, direction='FORWARD') for lon, lat in zip(lons, lats) ]
ellipsoidal_areas.append(Polygon(e_coords).area)
# transform the centre point to the projected CRS
px, py = transformer.transform(x, y, direction='FORWARD')
# construct a circle around the projected point on a plane, calculate area, append to list
p_coords = [ offset(px, py, r, az) for az in forward_azimuths ]
planar_areas.append(Polygon(p_coords).area)
# get radial distances frpm the centre to each of the 16 points on the circle
ellipsoidal_radial_distances = [ hypot(px - ex, py - ey) for ex, ey in e_coords ]
# get the sum of the distances, and the expected value for each distance
total_radial_dist = sum(ellipsoidal_radial_distances)
expected_distance = total_radial_dist / n
# get the difference between the actual and expected radial distance for each 'spoke'
shape_distortion = [ abs((expected_distance / total_radial_dist) - (d / total_radial_dist)) for d in ellipsoidal_radial_distances ]
shape_indices.append(sum(shape_distortion))
# calculate shape distortion
Es = sum(shape_indices) / len(shape_indices)
# calculate areal distortion
diff_sum = 0
for e, p in zip(ellipsoidal_areas, planar_areas):
diff_sum += abs(e - p) / abs(e + p)
Ea = 1 / sample_number * diff_sum
Ka = (1 + Ea) / (1 - Ea)
''' FINITE DISTANCE DISTORTION - Gosling & Symeonakis (2020) '''
# loop once per sample required
planar_distances = []
ellipsoidal_distances = []
for i in range(sample_number):
# get two random locations (x and y separately)
xs = uniform(low=minx, high=maxx, size=2)
ys = uniform(low=miny, high=maxy, size=2)
# calculate the distance along the ellipsoid
ellipsoidal_distances.append(g.line_length(xs, ys))
# transform the coordinates
origin = transformer.transform(xs[0], ys[0], direction='FORWARD')
destination = transformer.transform(xs[1], ys[1], direction='FORWARD')
# calculate the planar distance
planar_distances.append(hypot(origin[0] - destination[0], origin[1] - destination[1]))
# calculate distance distortion
diff_sum = 0
for e, p in zip(ellipsoidal_distances, planar_distances):
diff_sum += abs(e - p) / abs (e + p)
Ep = 1 / sample_number * diff_sum
# return all of the measures
return Ep, Es, Ea, Ka
# this block will only run if the script is executed directly
if __name__ == "__main__":
# set strings for ISO3 code (country) and proj string (projection)
iso_string = "GRL"
# set the projected CRS' to evaluate for distortion
proj_string = "+proj=eck4 +lon_0=0 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs" # Eckert IV (Equal Area)
# proj_string = "+proj=merc +a=6378137 +b=6378137 +lat_ts=0.0 +lon_0=0.0 +x_0=0.0 +y_0=0 +k=1.0 +units=m +nadgrids=@null +wktext +no_defs" # Web Mercator (Conformal)
# set the geographical proj string and ellipsoid (should be the same)
geo_string = "+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs" # WGS84
g = Geod(ellps='WGS84')
# load the shapefile of countries and extract country of interest
world = read_file("../data/natural-earth/ne_10m_admin_0_countries.shp")
# validation - exit if the country code is wrong
if iso_string not in list(world.ISO_A3):
print("WHOOPS! That country code does not exist")
exit()
# set country using country code
country = world.loc[world.ISO_A3 == iso_string]
# get the bounds of the country
minx, miny, maxx, maxy = country.total_bounds
# initialise a PyProj Transformer to transform coordinates
transformer = Transformer.from_crs(CRS.from_proj4(geo_string), CRS.from_proj4(proj_string), always_xy=True)
# calculate the distortion
Ep, Es, Ea, Ka = evaluate_distortion(g, transformer, minx, miny, maxx, maxy, 1000)
# report to user
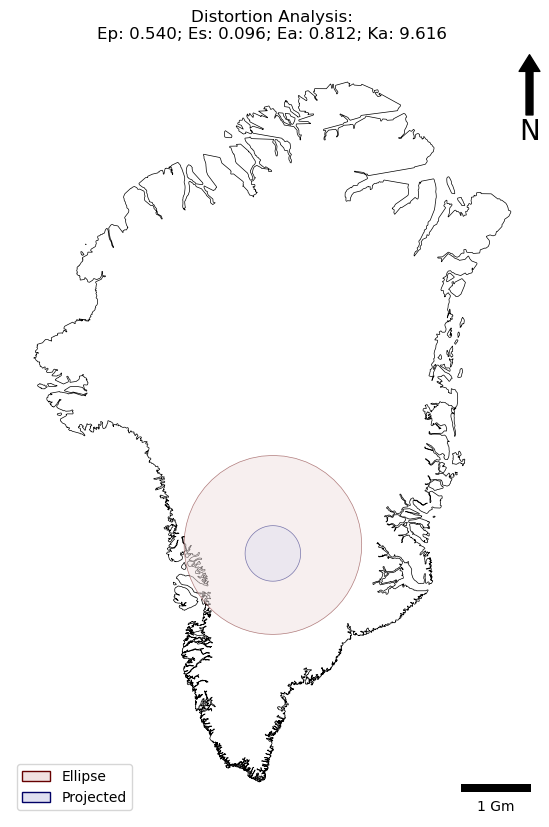
print(f"Distance distortion\t(Ep): {Ep:.6f}")
print(f"Shape distortion\t(Es): {Es:.6f}")
print(f"Area distortion\t\t(Ea): {Ea:.6f}")
print(f"Scale factor\t\t(Ka): {Ka:.6f}")
''' PLOT AN ILLUSTRATION ON A MAP '''
# calculate centre point
x_centre = minx + ((maxx - minx) / 2)
y_centre = miny + ((maxy - miny) / 2)
radius = 400000
# draw a circle on the ellipse and add make a GeoSeries
lons, lats = g.fwd([x_centre]*60, [y_centre]*60, list(range(0, 360, 6)), [radius]*60)[:2]
circle1 = Polygon([ transformer.transform(lon, lat, direction='FORWARD') for lon, lat in zip(lons, lats) ])
circle_1 = GeoSeries(circle1, crs=proj_string)
# draw a circle on the plane and add make a GeoSeries
x_centre, y_centre = transformer.transform(x_centre, y_centre, direction='FORWARD')
circle2 = Point(x_centre, y_centre).buffer(radius)
circle_2 = GeoSeries(circle2, crs=proj_string)
# create map axis object
fig, my_ax = subplots(1, 1, figsize=(16, 10))
my_ax.axis('off')
# set title
my_ax.set_title(f"Distortion Analysis:\nEp: {Ep:.3f}; Es: {Es:.3f}; Ea: {Ea:.3f}; Ka: {Ka:.3f}")
# plot country
country.to_crs(proj_string).plot(
ax = my_ax,
color = '#ffffff',
edgecolor = '#000000',
linewidth = 0.5,
)
# plot geographical circle
circle_1.plot(
ax = my_ax,
color = '#f0e0e0',
alpha = 0.5,
edgecolor = '#660000',
linewidth = 0.5,
)
# plot planar circle
circle_2.plot(
ax = my_ax,
color = '#e0e0f0',
alpha = 0.5,
edgecolor = '#000066',
linewidth = 0.5,
)
# manually draw a legend
my_ax.legend([
Patch(facecolor='#f0e0e0', edgecolor='#660000', label='Ellipse'),
Patch(facecolor='#e0e0f0', edgecolor='#000066', label='Projected')],
['Ellipse', 'Projected'], loc='lower left')
# add scalebar
my_ax.add_artist(ScaleBar(dx=1, units="m", location="lower right"))
# add north arrow
x, y, arrow_length = 0.99, 0.99, 0.1
my_ax.annotate('N', xy=(x, y), xytext=(x, y-arrow_length),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', width=5, headwidth=15),
ha='center', va='center', fontsize=20, xycoords=my_ax.transAxes)
# save the result
savefig('out/5.png', bbox_inches='tight')
print("done!")